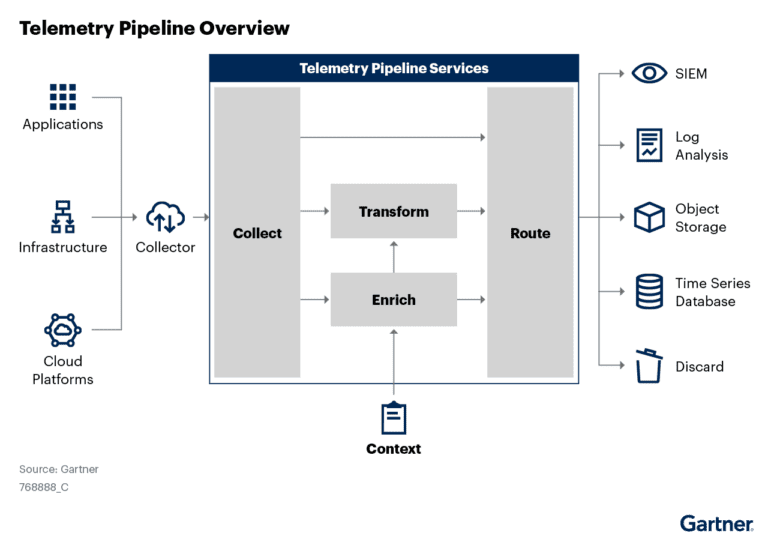
Data Centralization emerges as a necessity in the cloud world now that data is omnipresent. Gone are the days when different teams had to rely on document sharing and wait till the data gets to them. With AIOps, data can be centralized and teams can have access to it in near real-time.
This is a great opportunity for organizations to take advantage of the latest technology and leverage its power to solve their problems efficiently.
However, there are certain challenges that come along with this centralization approach. Data silos need to be broken down as redundant data affects the speed of the system.
Moreover, data needs to be correctly structured so that it can be easily accessed and used by all teams across the organization.
In this blog post, we will explore the obstacles and opportunities associated with data centralization in the context of AIOps and observability platforms.
What is Data Centralization?
Data centralization for observability platforms refers to the practice of aggregating data from various sources, such as logs, metrics, traces, and other relevant data points, into a centralized repository or platform. The goal is to consolidate and unify all observability data within a single location for streamlined analysis, monitoring, and decision-making processes.
Observability platforms collect data from different components of an IT system, including applications, services, infrastructure, and networks. This data is then ingested and stored centrally, allowing for comprehensive visibility and analysis of system behavior, performance, and issues.
Best Practices for Data Centralization
Data centralization has long been viewed as an effective means of gathering and analyzing information for business operations. However, it is important to recognize that centralized databases also come with their own set of challenges.
To address these challenges, platforms ought to utilize the following best practices:
- Comprehensive understanding of infrastructure: Organizations should have a deep understanding of their infrastructure to effectively leverage advanced analytics techniques like machine learning. This enables efficient solutions and improves the identification of patterns and anomalies in data.
- Utilizing big data for better decision-making: By harnessing big data, organizations can identify opportunities and make informed decisions. Implementing effective strategies ensures that technology investments yield a maximum return on investment.
- Considerations for security and privacy: Organizations must prioritize security and privacy when implementing digital initiatives. Taking adequate measures to protect data and resources is crucial due to the constant presence of security threats. Compliance with regulations like GDPR is necessary to safeguard individuals’ personal data.
- Compliance with regulations: Organizations must adhere to regulations such as GDPR, which safeguards the privacy of individuals’ personal data. Compliance ensures that organizations maintain ethical data handling practices and protect the privacy rights of individuals.
- Scalability planning: Consideration of scalability is essential when planning digital initiatives. Organizations should ensure that their systems can scale up or down based on demand. This flexibility ensures the system can accommodate future growth and changing requirements.
Obstacles and Opportunities for AIOps with Respect to Data Centralization
In the present time, the prevailing trend of data centralization allows seamless data sharing across all stakeholders, regardless of the varying permissions and access levels.
As organizations increasingly recognize the value of observability platforms and AIOps (Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations) in managing complex systems, they also encounter various challenges during the onboarding process.
One critical aspect of this process is data centralization, which involves aggregating data from diverse sources into a single platform for analysis and decision-making.
When onboarding a new observability platform, there can be several challenges that organizations commonly face. Here are some typical challenges:
Complexity
Steeped Learning Curve
Data Collection
Alerting and Noise Filtering
Data Integration
Support and Troubleshooting
Customization and Flexibility
Cultural Adoption
Scalability Issues
Security & Compliance
1. Complexity
The complexity of observability platforms poses a significant challenge during onboarding.
These platforms often offer a wide range of features, functionality, and configuration options, which can be overwhelming for new users. To overcome this obstacle, organizations should invest in comprehensive training and education programs to familiarize users with the platform and its capabilities.
Furthermore, simplifying the user interface and providing intuitive workflows can enhance the user experience and expedite adoption.
2. Data Collection
Effective data collection is crucial for AIOps and observability platforms. However, setting up proper data collection mechanisms can be challenging.
Organizations need to instrument their applications, services, and infrastructure to send relevant data to the observability platform. This process requires careful planning, coordination, and collaboration between development, operations, and data teams.
Automation and standardized instrumentation practices can streamline data collection and minimize manual effort.
3. Data Integration
Integrating the observability platform with existing systems and tools is a complex task. Organizations often need to connect various data sources, such as logs, metrics, and traces, to gain comprehensive insights.
Ensuring seamless integration and correlation of these disparate data sources within the platform can be a challenge.
Adopting standards-based approaches, leveraging APIs, and utilizing pre-built integrations can simplify the data integration process and maximize the value derived from observability data.
4. Scalability
Scalability is a critical consideration when centralizing data for AIOps. As systems and services expand, the observability platform must handle the growing volume of data effectively.
Organizations should evaluate the scalability features of their chosen platform, such as horizontal scaling, distributed storage, and auto-scaling capabilities.
Employing cloud-based solutions can provide the necessary infrastructure elasticity to accommodate increasing data loads.
5. Alerting and Noise Filtering
Configuring effective alerts and minimizing noise from false positives is a common challenge in AIOps. Determining the right thresholds, setting up meaningful alerts, and avoiding alert fatigue is essential during the onboarding process.
Machine learning techniques can help automate alert tuning and noise reduction, enabling organizations to focus on actionable insights. Continuous refinement of alerting rules based on historical data and feedback from operations teams can improve the accuracy and relevance of alerts.
6. Steep learning curve
Comprehensive training and education programs are essential for the successful adoption of observability platforms. Educating teams on the platform’s capabilities, best practices, and data analysis techniques can accelerate the onboarding process.
Organizations should invest in training resources, documentation, and workshops tailored to different user roles and skill levels. Hands-on exercises and real-world use cases can empower users to leverage the platform effectively and derive maximum value from the centralized data.
7. Cultural Adoption
Shifting the organization’s culture to embrace observability requires a change in mindset and behavior. Encouraging teams to proactively use the platform, share insights, and collaborate effectively is a significant challenge.
Leadership support, clear communication of goals and benefits, and fostering a culture of data-driven decision-making are crucial for successful cultural adoption. Recognizing and rewarding teams for their contributions to observability can motivate adoption and collaboration.
8. Customization and Flexibility
Tailoring the observability platform to meet specific organizational needs can be challenging. Organizations have unique requirements for custom dashboards, reports, and visualizations. The platform should offer flexible customization options, such as configurable widgets, APIs, and scripting capabilities.
Collaboration between data teams, platform vendors, and internal stakeholders can help identify customization requirements and implement tailored solutions.
9. Security and Compliance
Data centralization brings security and compliance considerations to the forefront. Ensuring the observability platform aligns with security requirements, including data encryption, access controls, and auditing, is essential.
Organizations must assess the platform’s security features and compliance certifications to ensure it meets their standards. Close collaboration between security, compliance, and platform teams is necessary to address any gaps and mitigate risks associated with data centralization.
10. Support and Troubleshooting
Timely support and troubleshooting assistance from the platform vendor are critical during the onboarding process. Organizations should establish effective communication channels and support systems to address user queries and resolve issues promptly.
Proactive engagement with the vendor’s support team, leveraging online forums and communities, and sharing feedback on platform usability can help enhance the support experience. Additionally, maintaining an internal troubleshooting knowledge base can empower users to troubleshoot common issues independently.
How Apica uses AIOps for Centralized Observability
Observability plays a crucial role in AIOps as it empowers IT, teams, to promptly detect and resolve issues in real-time, eliminating the need to rely solely on user-reported problems.
Through the collection of data from diverse sources such as infrastructure, application logs, and network traffic, centralized observability offers comprehensive system visibility. This comprehensive view enables IT teams to swiftly identify and address problems, ensuring efficient troubleshooting and resolution.
Apica harnesses the power of AIOps and observability to enhance enterprise IT environment management. By utilizing machine learning algorithms to analyze extensive data generated by systems and applications, Apica’s AIOps capabilities enable the detection of anomalies and potential issues at an early stage. This proactive approach empowers IT teams to promptly address problems, minimizing downtime and optimizing system performance.
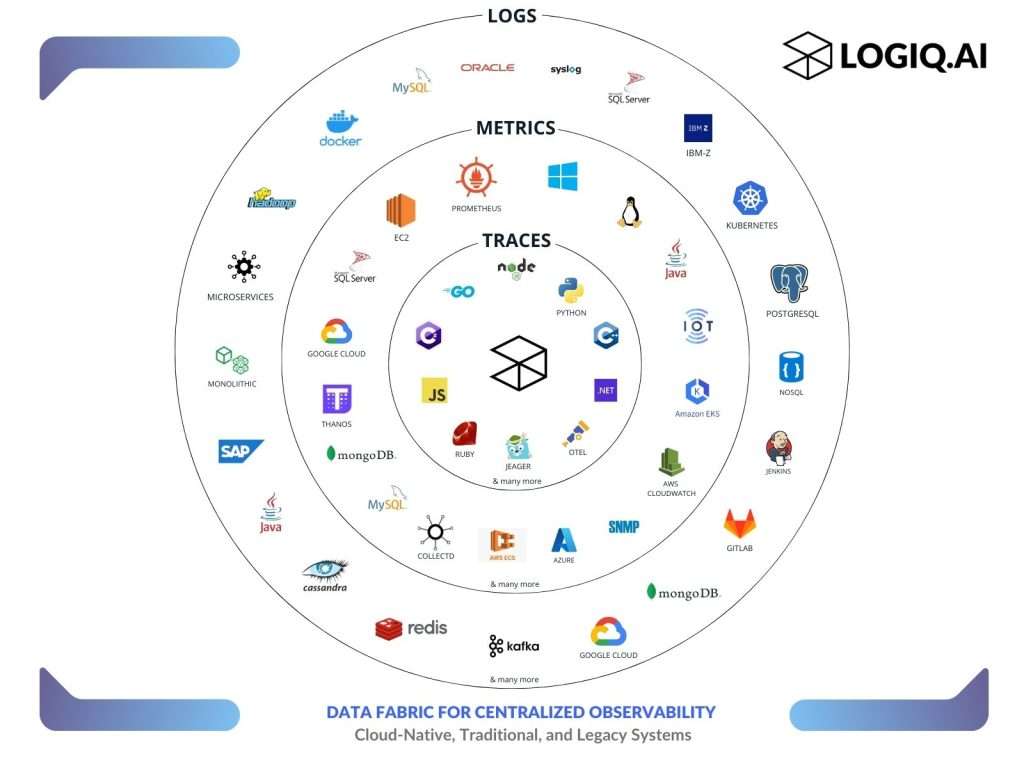
Apica’s AIOps capabilities encompass:
1. Anomaly Detection: Leveraging machine learning algorithms, Apica detects deviations in system behavior, providing early alerts to IT teams for potential issues that could escalate into significant problems.
2. Root Cause Analysis: By automatically analyzing data from multiple sources, Apica identifies the root cause of issues, reducing the mean time to resolution (MTTR) for IT incidents and expediting problem-solving.
3. Predictive Analytics: Employs historical data analysis to predict future performance issues and offers recommendations on preventive actions to mitigate such issues.
4. Automated Remediation: Automates incident response processes, such as restarting services or scaling resources, based on predefined rules and policies. This streamlines incident resolution and reduces manual intervention.
5. Intelligent Alerting: Apica’s intelligent alerting mechanism ensures that IT teams receive relevant alerts tailored to their roles and responsibilities, mitigating alert fatigue and improving incident response times.
6. Capacity Planning: Facilitates capacity planning by forecasting resource utilization trends, assisting organizations in optimizing their infrastructure capacity to meet demand while minimizing costs.
Wrapping Up
While data centralization has its merits, it is important to be aware of its limitations. Organizations must carefully consider the drawbacks associated with centralized databases, including increased workload, reduced location-based adaptability, limited input diversity, the risk of data loss, and higher costs.
Moreover, data centralization is a key component of successful AIOps and observability platform adoption. And though it presents various challenges, organizations can overcome them by implementing a well-defined onboarding plan, involving key stakeholders from the beginning, providing comprehensive training and support resources, and establishing a feedback loop for continuous improvement.
Organizations can unlock the full potential of AIOps by addressing these obstacles and capitalizing on the opportunities. This will lead to enhanced operational efficiency, proactive incident management, and improved customer experiences.
Through the aforementioned AIOps capabilities, apica.io enables enterprises to proactively manage their IT environments with enhanced efficiency and effectiveness. Thus, organizations can achieve improved operational outcomes by minimizing downtime and optimizing system performance.
In a Glimpse
- Data centralization with AIOps enables real-time data access and efficient problem-solving.
- Challenges: Breaking down data silos, and ensuring proper data structure.
- Best practices: Understand infrastructure, utilize big data, prioritize security and compliance, and plan for scalability.
- AIOps obstacles: Complexity, data collection, integration, scalability, alerting, learning curve, cultural adoption, customization, security, and support.
- Apica’s AIOps: Anomaly detection, root cause analysis, predictive analytics, automated remediation, intelligent alerting, capacity planning.
- Consider the limitations and drawbacks of data centralization.
- Overcome challenges through planning, training, stakeholder involvement, and continuous improvement.
- AIOps with data centralization improve efficiency, incident management, and customer experiences.