Find out what is an Operational Data Fabric and what is it about. Get a detailed explanation of what are the key challenges, advantages, and capabilities.
According to a GRAND VIEW RESEARCH report, the worldwide data fabric market was worth $1,399.7 million in 2021 and is forecast to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 21.2% from 2022 to 2030. Thus, with the remarkable growth of data fabrics, the Operational Data Fabric has undisputed potential in the Big Data landscape. Let’s see how.
Enterprises today are facing a growing challenge when it comes to managing large amounts of complex and diverse data. The traditional approaches to data management, such as siloed databases, are no longer adequate to meet the demands of modern businesses. This is where the concept of an operational data fabric comes into play. In this article, we will discuss what operational data is, why it is a must-have for enterprises, and its key benefits.
An operational data fabric is a modern and integrated approach to data management that enables businesses to efficiently store, manage, and process large amounts of complex and diverse data. It is designed to provide a single, unified view of all data, regardless of its source, format, or location. It also integrates data from various sources, such as databases, cloud storage, IoT devices, and more, and provides a centralized platform for data management.
Additionally, it allows for rapid insights into the most complex datasets by seamlessly connecting different databases and applications. This helps to bridge the gap between different siloed data sources, allowing for rapid access and analysis of data.
What is Operational Data?
Operational data refers to the data generated and used by an organization in the course of day-to-day operations, typically by systems and applications to support business processes. This data is often transactional in nature and can include information such as customer orders, inventory levels, financial transactions, and log data from systems and applications. Operational data is usually contrasted with analytical data, which is specifically collected and organized for use in business intelligence and analysis.
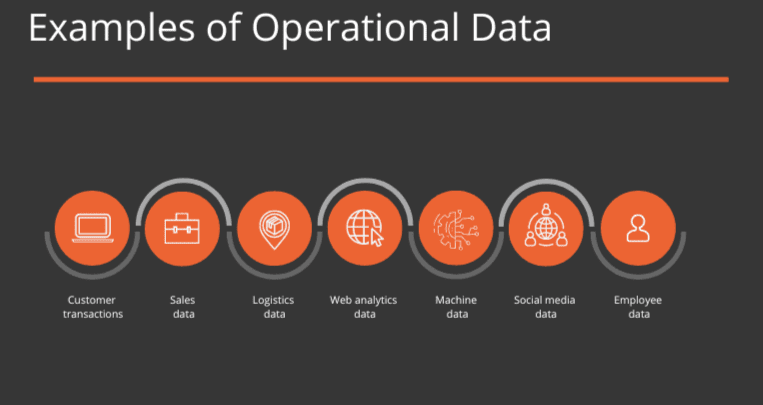
The following are a few examples of operational data:
- Customer transactions: Data on customer purchases, payments, and other transactional activities.
- Inventory levels: Data on the stock levels of products, raw materials, and other items.
- Sales data: Data on the sales of products or services, including customer demographics, sales channels, and other relevant information.
- Logistics data: Data on the movement of goods, shipping times, and delivery status.
- Employee data: Employee information, including demographics, job roles, and performance metrics.
- Machine data: Data from sensors and other monitoring devices that provide information on machine performance and usage.
- Environmental data: Data on environmental factors, such as temperature, humidity, and air quality.
- Energy usage data: Data about energy consumption, production, and distribution.
- Social media data: Data from social media platforms, such as Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram.
- Web analytics data: Website traffic, user behavior, and engagement metrics.
These are a few examples of operational data, which can come from a wide range of sources and can be used to support a wide range of business activities. By collecting, storing, and analyzing operational data, organizations can gain valuable insights into their operations and make data-driven decisions that drive business value.
Benefits of apica.io as an Operational Data Fabric
Reduce cost and complexity by 90% with Apica
The Apica observability platform works on a data fabric architecture. apica.io connects all of your real-time operational data – including business, observability, security, and network – with its innovative zero-archive architecture. This fabric unifies your data and provides you with instant insights, control, and compliance at scale, which aims to provide the following benefits:
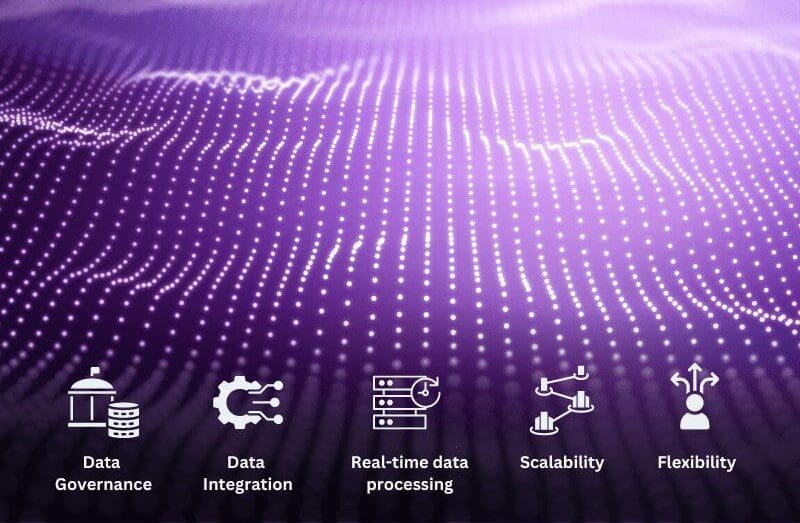
Data Integration: Provides a unified platform for integrating and managing data from disparate sources, reducing the complexity and cost of data integration.
Real-time data processing: With its real-time data processing capabilities, Apica enables organizations to make data-driven decisions quickly, improving the speed and efficiency of operations.
Data Governance: Provides robust data governance capabilities, such as data cataloging, metadata management, and data lineage, which can help organizations manage data quality and ensure data privacy and security.
Scalability: Designed to scale with growing data volumes, enabling organizations to accommodate increased data-driven demands without adding complexity.
Flexibility: The flexible architecture allows organizations to easily add or change data sources, making it easier to adapt to changing business requirements.
Why is an Operational Data Fabric a Must-Have for Enterprises?
The advantages of an operational data fabric are numerous. For businesses, it allows them to quickly draw insights from their various datasets and make informed decisions faster than ever before. It also enables better collaboration among teams and departments by providing a unified view of data. Moreover, it helps to reduce complexity and cost by eliminating redundant and inefficient software solutions, enabling organizations to focus on their core functions.
An operational data fabric also provides better security for companies as the data is stored in one place rather than spread out across different platforms. This reduces the risk of accidental or malicious data loss and allows for easier access control. Further, adopting the data mesh architecture can help organizations better manage their data and ensure its integrity across multiple systems. With an operational data fabric, companies can have the confidence that their data is safe, secure, and available for use whenever it’s needed.
The following points highlight the significance of using an operational data fabric for enterprises:
- Improved Data Integration: An operational data fabric helps to integrate data from disparate sources, making it easier for businesses to manage their data. This reduces the time and effort required to extract, transform, and load (ETL) data into various databases, as well as reducing the risk of data loss or corruption.
- Enhanced Data Governance: An operational data fabric helps to enforce data governance policies, such as data privacy, security, and compliance. It provides a centralized platform for managing data and ensures that data is protected and secure.
- Increased Data Analytics Capabilities: An operational data fabric provides businesses with a comprehensive view of their data, making it easier for them to gain insights and make informed decisions. By integrating data from multiple sources, businesses can access a wider range of data for analysis and improve the accuracy of their insights.
- Scalability and Flexibility: An operational data fabric is designed to scale and adapt to the changing needs of businesses. It provides a flexible and scalable platform that can accommodate growth and changing business requirements.
- Cost Savings: An operational data fabric can help businesses save on costs by reducing the need for multiple databases, cloud storage solutions, and other data management tools. This, in turn, reduces the need for additional hardware, software, and personnel, leading to cost savings.
- Enhanced Data Security: An operational data fabric enables organizations to secure and manage sensitive data, reducing the risk of data breaches.
- Improved Data Analytics: An operational data fabric provides organizations with a centralized and integrated data infrastructure, enabling them to perform more advanced and sophisticated data analytics.
- Better Customer Experience: An operational data fabric enables organizations to use data to better understand their customers and improve the customer experience.
- Cost Savings: By improving data quality and reducing the time to insight, organizations can reduce their overall costs and improve their bottom line.
- Competitive Advantage: An operational data fabric enables organizations to make better use of their data, giving them a competitive advantage over organizations that do not have a similar infrastructure.
Benefits of an Operational Data Fabric
Some of the key advantages of an operational data fabric include:
- Improved Data Quality: An operational data fabric helps to improve the quality of data by providing a centralized platform for data management. This reduces the risk of data loss or corruption and ensures that data is accurate and up-to-date.
- Real-Time Data Processing: An operational data fabric enables real-time data processing, providing businesses with the ability to quickly respond to changing business conditions. This helps to improve the speed and efficiency of decision-making processes.
- Better Data Security: An operational data fabric provides businesses with a secure platform for data management. It helps to protect data against cyber threats and ensures that data is only accessible by authorized personnel.
- Increased Collaboration: An operational data fabric provides a centralized platform for data management, making it easier for teams to collaborate and share data. This helps to improve the speed and efficiency of decision-making processes and promotes better collaboration among teams.
- Improved operational efficiency: An operational data fabric enables organizations to streamline data-related processes, improving operational efficiency and reducing costs.
- Better decision-making: An operational data fabric provides organizations with better access to data, enabling them to make informed business decisions and drive growth.
Importance of an operational data fabric in Data Engineering
An operational data fabric plays a crucial role in data engineering as it acts as the underlying infrastructure that connects different data sources, storage systems, and analytics tools. It helps organizations efficiently manage and process their data, ensuring that the data is accessible, secure, and available for analysis.
Some key benefits of an operational data fabric include:
- Data Integration: An operational data fabric enables organizations to integrate data from disparate sources into a single, unified view, making it easier to analyze and make data-driven decisions.
- Scalability: As data grows, an operational data fabric can handle the increase in volume, velocity, and variety of data, making it easier for organizations to scale their data infrastructure as needed.
- Data Management: An operational data fabric provides a centralized, streamlined approach to data management, making it easier to maintain the quality, consistency, and security of data across the organization.
- Improved Analytics: By providing a centralized platform for data integration, an operational data fabric enables organizations to perform more advanced analytics, such as machine learning, to uncover hidden patterns and relationships in their data.
- Cost Savings: An operational data fabric can help organizations reduce costs associated with data management and analysis by eliminating the need for manual data management processes and reducing the need for multiple data storage systems.
Size of Operational data vs Database data
It’s difficult to quantify the size difference between operational data and data stored in databases as it can vary greatly depending on the specific organization and its data needs. However, in general, operational data is often larger than data stored in databases due to the large volume of real-time data generated by business operations, such as transactions, machine data, and other sources.
While databases are designed to store structured data, operational data can be more complex and unstructured, requiring specialized systems and tools to process and analyze it. As a result, operational data may need to be stored in separate data lakes or data warehouses, rather than in databases.
It’s important to note that not all operational data needs to be stored in databases, and organizations can choose to store only the data that is critical for their operations and decision-making. The specific size difference between operational data and data stored in databases will depend on the organization’s data management strategy and infrastructure.
Bottomline
“Data fabric is not merely a combination of traditional and contemporary technologies but a design concept that changes the focus of human and machine workloads.”– Gartner
It is pretty much evident that the data fabric architecture is critical for organizations looking to unlock the full potential of their data and drive digital transformation. By providing a unified view of data and enabling organizations to connect, manage, and use data at scale, an operational data fabric is a key enabler of data-driven decision-making and business value.
In conclusion, it is a must-have for enterprises looking to efficiently store, manage, and process large amounts of complex and diverse data. With its improved data integration, enhanced data governance, increased data analytics capabilities, scalability and flexibility, and cost savings, Apica’s data fabric provides a modern and integrated approach to data management.
In a Glimpse:
- An Operational Data Fabric is a modern and integrated approach to data management that enables businesses to store, manage, and process large amounts of complex and diverse data.
- It provides improved integration of disparate sources, enhanced governance policies such as security & compliance, increased analytics capabilities with a unified view of all the datasets for analysis & insights, scalability & flexibility, cost savings, and better customer experience.
- Apica is an operational data fabric that offers features such as real-time processing capabilities for faster decision-making processes and robust security solutions like metadata management.
- An operational data fabric empowers organizations to leverage their assets in real-time driving innovation while providing a competitive advantage over other enterprises.